
Presently, WebSocket and WebRTC are key technologies being used for building modern, low-latency web apps. In this article we are going to explore the differences between two technologies and look at trade-offs
Table of Contents
- Introduction to WebSockets
- Introduction to WebRTC
- WebRTC vs WebSockets - What are the key differences
- When to use WebSockets?
- When to use WebRTC?
- When to use WebRTC and WebSockets together?
Introduction to WebSocket?
WebSocket is a realtime technology that enables bi-directional, full-duplex communication between a client and server over a stateful, persistent, single socket connection.
A WebSocket connection starts with an HTTP request/response handshake. Once this handshake is successful, the client and the server agrees to use the existing TCP connection that was established for the HTTP request as a WebSocket connection.
This connection is kept stateful/alive for as long as needed, allowing the server and the client to independently send data at will.
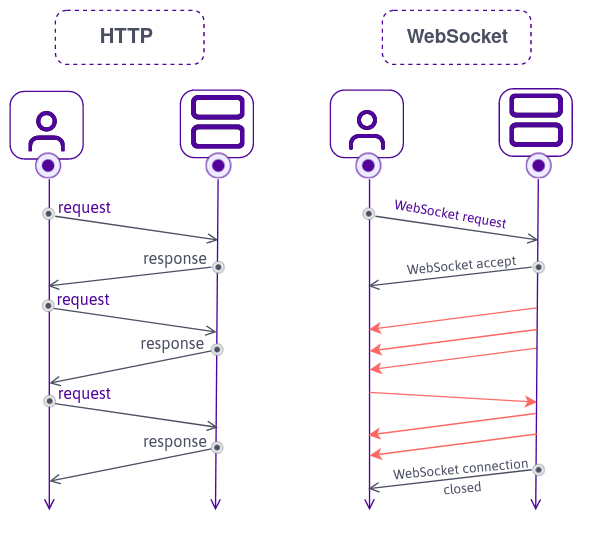
The WebSocket Technology includes two core building blocks:
The WebSocket protocol: The WebSocket Protocol (RFC 6455), standardized in December 2011. The WebSocket protocol enables realtime communication between a WebSocket client and a WebSocket server over the web. It supports transmission of binary data and text strings.
The WebSocket API: The WebSocket API, allows you to perform necessary actions, i.e. managing WebSocket connection, receiving and sending messages, and listening events triggered by the WebSocket server. Most of modern era web-browsers support the WebSocket API. Read more about WebSocket API on Mozilla Developer
Advantages of WebSockets
Prior to WebSocket, HTTP techniques like AJAX long-polling and Comet were the standard for building realtime applications. Compared to HTTP connection, WebSocket; being stateful, eliminates the need for a new connection with every request, drastically reducing the size of each message (no HTTP headers). This saves bandwidth, improves latency and connection cheaper than HTTP.
Flexibility is ingrained into the design of the WebSocket technology. This allows for the implementation of application-level protocols and extensions for additional functionality (i.e. as pub/sub messaging).
WebSocket being an event-driven technology, WebSocket allows data to be transferred without the client requesting it (push). This characteristic is desirable in scenarios where the client needs to react quickly to an event (especially ones it cannot predict, i.e new message, maintenance alert, fraud alert).
Disadvantages of WebSocket
WebSocket is stateful. This can be tricky to handle, especially at scale, because it requires the server layer to keep track of each individual open WebSocket connection and maintain their state information.
WebSockets don’t automatically recover when connections are terminated – this is something you need to implement yourself. This is the reason, why there are many WebSocket client-side libraries in existence.
Certain environments will block WebSocket connections for security reasons (i.e Corporate networks with proxy servers)
Introduction to WebRTC?
On the other hand, Web Real-Time Communication (WebRTC) is a framework that enables you to add real time communication (RTC) capabilities to your web and mobile applications.
In comparison with WebSocket, WebRTC allows the transmission of arbitrary data (video, voice, and generic data) in a peer-to-peer connection.
Most of the modern browser supports WebRTC. In addition, in case WebRTC are not supported than there are many WebRTC SDK targeting different platforms (i.e iOS and Android) are available. WebRTC consists of several inter-related APIs. Here are the important ones:
RTCPeerConnection: RTCPeerConnection allows us to connect to a remote peer, manage and monitor the connection, and close it once its purpose has been fulfilled.RTCDataChannel: RTCDataChannel provides a bi-directional network communication channel that allows peers to transfer arbitrary data.MediaStream: MediaStream is designed to let us access streams of media from local input devices i.e microphones, and cameras. It serves as a way to manage actions on a data streams, like recording, sending, resizing, and displaying the stream’s content.
Read more about WebRTC APIs on Mozilla Developer
Advantages of WebRTC
WebRTC encrypt and authenticate data transferred over WebRTC using Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (SRTP), making it more secure protocol compared to other protocols available.
WebRTC is open-source and free to use. The project is backed by a strong and active community, and it’s backed by reputed and stable organizations such as Apple, Google, and Microsoft.
WebRTC is platform and device neutral. A WebRTC application will work on any browser that supports WebRTC, irrespective of operating systems or the type of devices.
Disadvantages of WebRTC
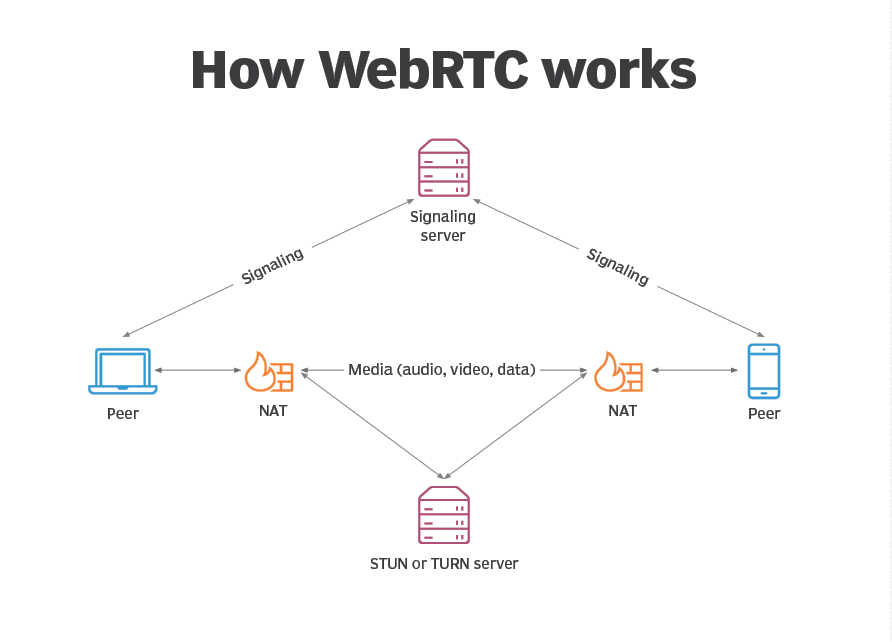
Even though WebRTC is a peer-to-peer technology, you still have to manage and pay for web servers. For two peers to talk to each other, you need to use a signalling server to set up, manage, and terminate the WebRTC communication session. In one-to-many WebRTC broadcast scenarios, you’ll probably need a WebRTC media server to act as a multimedia middleware.
WebRTC can be extremely CPU-intensive, especially when dealing with video content and large groups of users. This makes it costly and hard to reliably use and scale WebRTC applications.
WebRTC is hard to get started with. There are plenty of concepts you need to explore and master: the various WebRTC interfaces, codecs & media processing, network address translations (NATs) & firewalls, UDP (the main underlying communications protocol used by WebRTC), and many more.
WebRTC vs WebSockets: What are the key differences?
WebSocket provides a client-server device communication protocol, whereas WebRTC offers a peer-to-peer protocol and communication capabilities for browsers and mobile applications. While WebSocket works only over TCP, WebRTC is primarily used over UDP (although it can work over TCP as well).
WebSocket is a better choice when data integrity is crucial, as you benefit from the underlying reliability of TCP. On the other hand, if speed is more important and losing some packets is acceptable, WebRTC over UDP is a better choice.
WebRTC is primarily designed for streaming audio and video content. It is possible to stream media with WebSockets too, but the WebSocket technology is better suited for transmitting text/string data using formats such as JSON.
When to use WebSockets?
We can broadly group Web Sockets use cases into two distinct categories:
Realtime Updates: where the communication is unidirectional, and the server is streaming low-latency (and often frequent) updates to the client. Think of live score updates or alerts and notifications, to name just a few use cases.
Bidirectional Communication: where both the client and the server send and receive messages. Examples include chat, virtual events, and virtual classrooms (the last two usually involve features like live polls, quizzes, and Q&As). WebSockets can also be used to underpin multi-user synchronized collaboration functionality, such as multiple people editing the same document simultaneously.
When to use WebRTC?
WebRTC is a good choice for Audio and video communications, such as video calls, video chat, video conferencing, and browser-based VoIP. For example:
- Screen sharing applications
- File sharing applications
- Broadcasting live events (such as sports events).
- IoT devices (i.e drones or baby monitors streaming live audio and video data).
When to use WebRTC and WebSocket together?
WebSockets and WebRTC are complementary technologies. As mentioned before, WebRTC allows for peer-to-peer communication, but it still needs servers, so that these peers can coordinate communication, through a process called signaling. Generally, signaling involves transferring information such as media metadata (e.g., codecs and media types), network data (for example, the host’s IP address and port), and session-control messages for opening and closing communication.
Keep one thing in mind, WebRTC does not provide a standard signaling implementation, allowing developers to use different protocols for this purpose. The WebSocket protocol is often used as a signaling mechanism for WebRTC applications, allowing peers to exchange network and media metadata in realtime.
About The Author
I am Pankaj Baagwan, a System Design Architect. A Computer Scientist by heart, process enthusiast, and open source author/contributor/writer. Advocates Karma. Love working with cutting edge, fascinating, open source technologies.
To consult Pankaj Bagwan on System Design, Cyber Security and Application Development, SEO and SMO, please reach out at me[at]bagwanpankaj[dot]com
For promotion/advertisement of your services and products on this blog, please reach out at me[at]bagwanpankaj[dot]com
Stay tuned <3. Signing off for RAAM
